Breaking Down BariClip: The Innovative Solution to Weight Loss Surgery
For those of us who struggle with severe obesity, weight loss surgery can be a life-changing solution. However, traditional weight loss surgery techniques can be invasive, risky, and require a long recovery time.
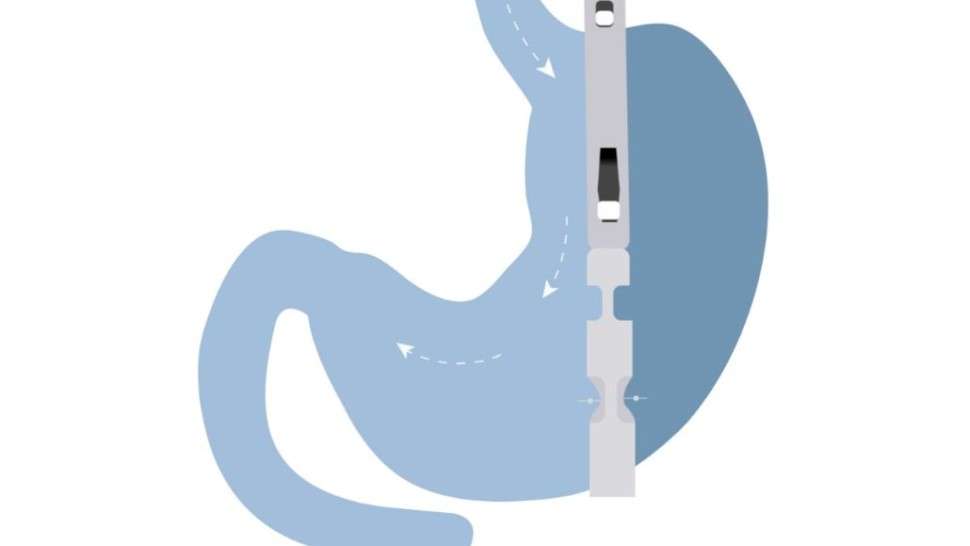
That's where Bariclip comes in - an innovative solution to weight loss surgery that is changing the game
Sommaire
- What is the BariClip?
- Understanding the Need for Weight Loss Surgery
- Limitations of Traditional Weight Loss Surgery Techniques
- What is Bariclip and How Does it Work?
- Advantages of Bariclip Over Traditional Weight Loss Surgery Techniques
- Risks and Complications Associated with Bariclip
- The Bariclip Procedure and Recovery Process
- Success Stories of Patients Who Underwent Bariclip
- Cost of Bariclip and Insurance Coverage
- Conclusion: Is Bariclip the Right Weight Loss Surgery Option for You?
- Sources



